By way of the wanting glass: On Friday, the otto-js Analysis Group printed an article outlining how customers leveraging Google Chrome or Microsoft Edge’s enhanced spelling options could also be unknowingly transmitting passwords and personally identifiable data (PII) to third-party cloud-based servers. The vulnerability not solely places the common finish consumer’s non-public data in danger, however it will possibly additionally depart a company’s administrative credentials and different infrastructure-related data uncovered to unauthorized events.
The vulnerability was found by otto-js co-founder and Chief Technical Officer (CTO) Josh Summit whereas testing the corporate’s script habits detection capabilities. Throughout the testing, Summit and the otto-js workforce discovered that the precise mixture of options in Chrome’s enhanced spell verify or Edge’s MS Editor will unintentionally expose subject knowledge containing PII and different delicate data, sending it again to Microsoft and Google servers. Each options require customers to take express motion to allow them, and as soon as enabled, customers are sometimes unaware that their knowledge is being shared with third events.
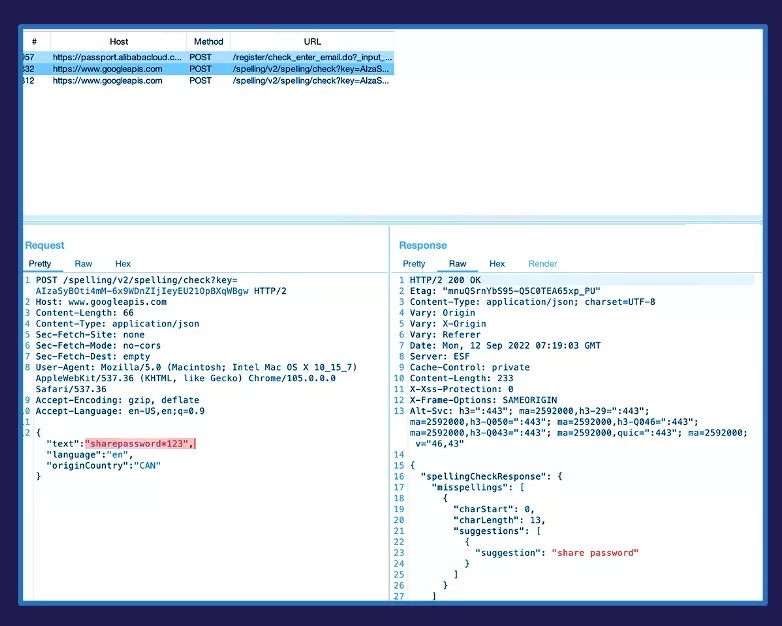
Along with subject knowledge, the otto-js workforce additionally found consumer passwords is likely to be topic to publicity by way of the view password choice. The choice, meant to assist customers in making certain passwords usually are not incorrectly keyed, inadvertently exposes the password to the third-party servers via the improved spell verify capabilities.
Particular person customers usually are not the one events in danger. The vulnerability may end up in company organizations having their credentials compromised by unauthorized third events. The otto-js workforce offered the next examples to point out how customers logging into cloud providers and infrastructure accounts can have their account entry credentials unknowingly handed to Microsoft or Google servers.
The primary picture (above) represents a pattern Alibaba Clout Account login. When logging in by way of Chrome, the improved spell verify operate passes request data to Google-based servers with out an administrator’s authorization. As seen within the screenshot under, this request data contains the precise password being entered for the corporate’s cloud login. Entry to such a data may end up in something from stolen company and buyer knowledge to the entire compromise of vital infrastructure.
The otto-js workforce performed testing and evaluation throughout management teams targeted on social media, workplace instruments, healthcare, authorities, ecommerce, and banking/monetary providers. Greater than 96% of the 30 management teams examined despatched knowledge again to Microsoft and Google. 73% of these websites and teams examined despatched passwords to the third-party servers when the present password choice was chosen. These websites and providers that didn’t have been those that merely lacked the present password operate and weren’t essentially correctly mitigated.
The otto-js workforce reached out to Microsoft 365, Alibaba Cloud, Google Cloud, AWS, and LastPass, which symbolize the highest 5 websites and cloud service suppliers presenting the best danger publicity to their company prospects. Based on the safety firm’s updates, each AWS and LastPass have already responded and indicated that the problem was efficiently mitigated.
Picture credit score: Magnifying Glass by Agence Olloweb; vulnerability screenshots by otto-js

